The space industry has seen countless technological leaps, but few have been as impactful as SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. Since its introduction, Falcon 9 has not only altered the trajectory of space travel but also redefined how humanity envisions the future of space exploration. It’s a symbol of innovation, cost efficiency, and the relentless pursuit of making space accessible to all.

A Vision Brought to Life
Falcon 9 is the flagship rocket developed by SpaceX, the private aerospace company founded by Elon Musk in 2002. Its mission? To make space exploration more affordable and sustainable. Named after the Millennium Falcon from “Star Wars,” and with “9” signifying the nine engines in its first stage, Falcon 9 was designed with reusability in mind. This concept, which was once considered far-fetched, became a reality through rigorous testing, engineering ingenuity, and groundbreaking technology.
The first successful launch of Falcon 9 took place on June 4, 2010. Since then, it has become the workhorse of SpaceX, carrying satellites, cargo, and astronauts into space. Notably, in 2012, Falcon 9 became the first commercial rocket to deliver cargo to the International Space Station (ISS), showcasing its capability to compete with, and even surpass, government-operated space programs.
Reusability: Changing the Game
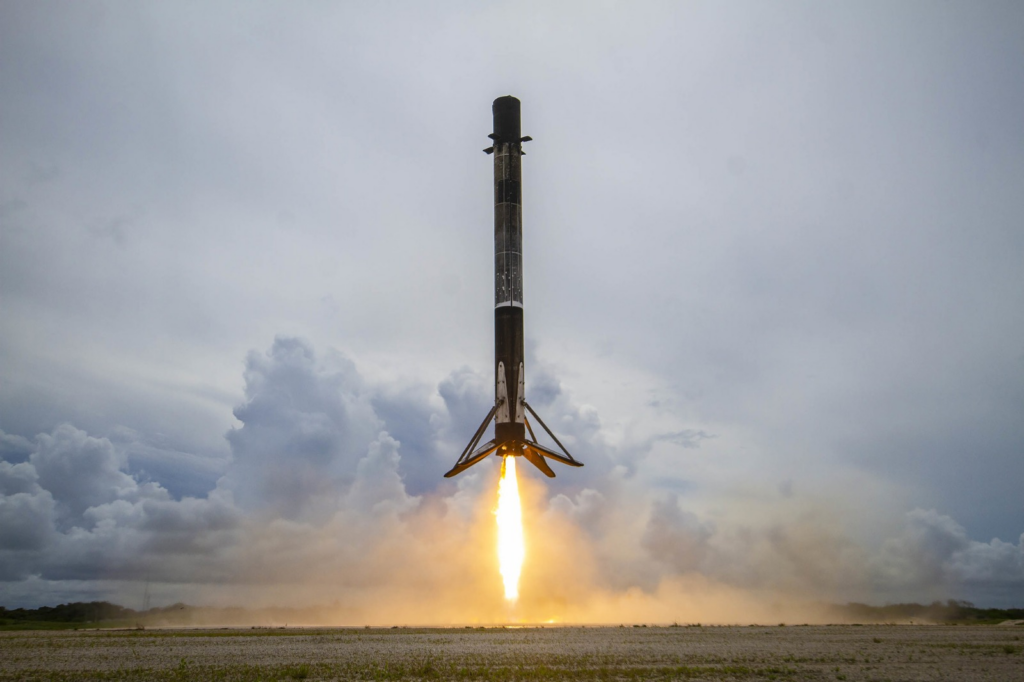
The defining feature of Falcon 9 is its ability to be reused. Traditionally, rockets have been single-use vehicles—discarded into the ocean after launching their payloads. This has contributed to the high cost of space missions. Falcon 9 changed that dynamic by designing a first stage that can return to Earth, land vertically, and be refurbished for future launches.
This ability to reuse rockets dramatically lowers costs and allows for quicker turnaround times between launches. In March 2017, SpaceX re-launched a previously flown Falcon 9 booster, marking a major milestone in the space industry and proving that reusable rockets are not only possible but practical. This shift in technology has brought the cost of space access down significantly, thereby encouraging more private companies and research institutions to participate in space endeavors.
Design and Performance
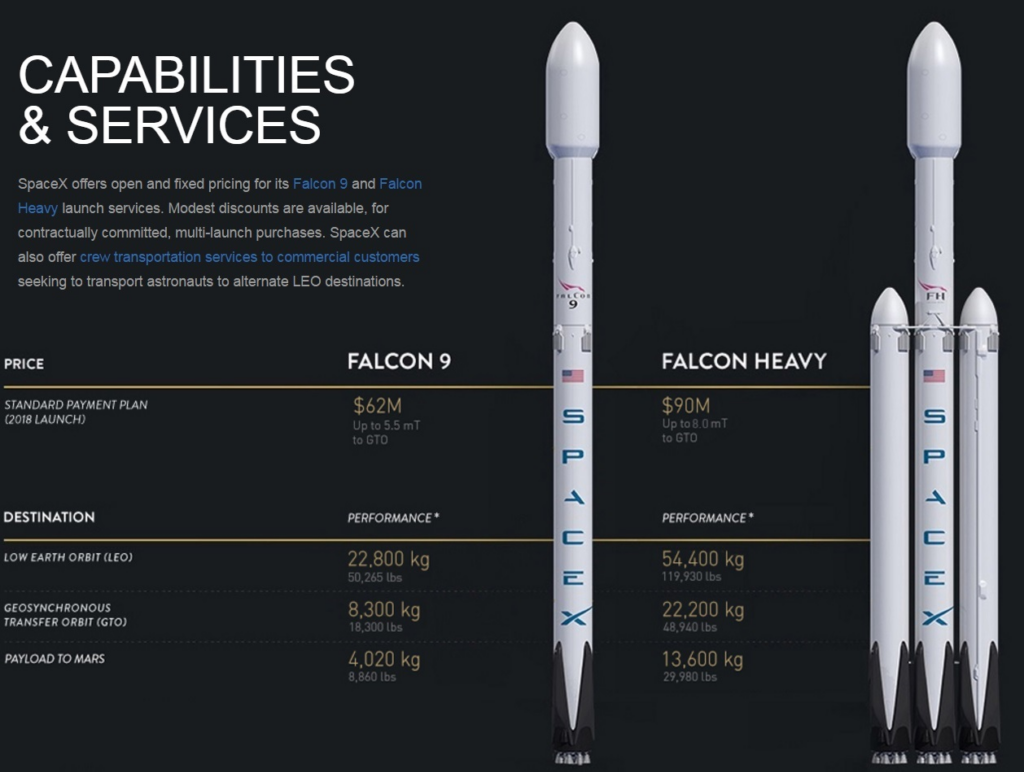
Falcon 9 stands over 70 meters tall, with a sleek two-stage configuration. The first stage is powered by nine Merlin engines, which use RP-1 (a refined form of kerosene) and liquid oxygen, providing a combined thrust of over 7.6 million newtons. This powerful thrust allows Falcon 9 to carry payloads weighing up to 22,800 kilograms to low Earth orbit (LEO).
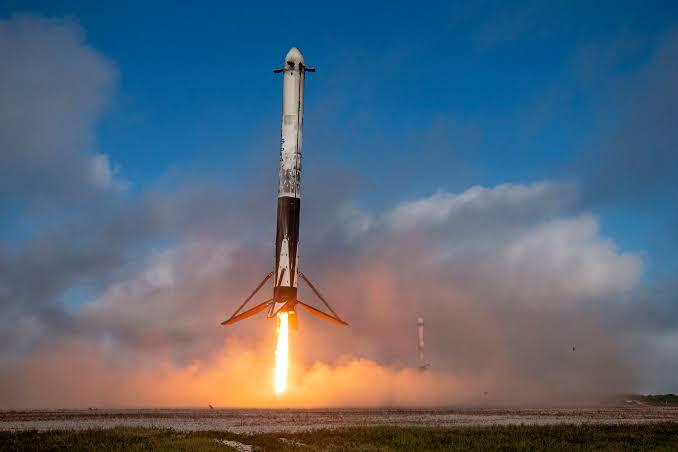
The second stage is equipped with a single Merlin Vacuum engine that propels the payload further into space once the first stage has detached. One of the defining moments of every Falcon 9 launch is the precision landing of the first stage, either on a drone ship in the ocean or on a landing pad on land. These controlled landings demonstrate the advanced engineering that underpins Falcon 9’s success and have become a hallmark of SpaceX missions.
Human Spaceflight and Beyond
Falcon 9 isn’t just a cargo carrier; it has played a pivotal role in the resurgence of American crewed spaceflight. In May 2020, the Crew Dragon spacecraft, launched atop a Falcon 9, carried NASA astronauts Doug Hurley and Bob Behnken to the ISS. This marked the first crewed orbital launch from U.S. soil since the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011.
Beyond Earth, Falcon 9 has also been instrumental in SpaceX’s Starlink initiative—a constellation of satellites designed to provide high-speed internet to remote areas worldwide. The sheer frequency of Falcon 9 launches for Starlink has cemented its reputation as one of the most reliable and versatile rockets in the industry.
A Glimpse Into the Future
Falcon 9’s success has paved the way for SpaceX’s larger ambitions, such as the development of the Starship rocket, which aims to take humanity to Mars. The lessons learned from Falcon 9—particularly around reusability and cost efficiency—are key elements that inform the design of future spacecraft. With its ongoing missions, Falcon 9 continues to demonstrate that affordable, frequent access to space is not only possible but is quickly becoming a reality.
Conclusion
Falcon 9 represents a pivotal moment in space exploration, merging innovation, vision, and practicality into a single launch vehicle. Its impact stretches beyond just SpaceX—it has inspired a new era of competition and collaboration within the aerospace industry. With its reusable design, consistent performance, and ability to safely carry both cargo and astronauts, Falcon 9 has redefined what we expect from rockets and has laid a strong foundation for humanity’s future in the stars.
The sky is no longer the limit, and Falcon 9 is proof of how far we can go when we dare to dream big.
